http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bloom%27s_Taxonomy
Bloom's Taxonomy
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
It refers to a classification of the different objectives that educators set for students (learning objectives). Bloom's Taxonomy divides educational objectives into three "domains": Cognitive, Affective, and Psychomotor (sometimes loosely described as knowing/head, feeling/heart and doing/hands respectively). Within the domains, learning at the higher levels is dependent on having attained prerequisite knowledge and skills at lower levels.[4] A goal of Bloom's Taxonomy is to motivate educators to focus on all three domains, creating a more holistic form of education.[1]
A revised version of the taxonomy was created in 2000.[5][6][7]
Bloom's Taxonomy is considered to be a foundational and essential element within the education community as evidenced in the 1981 survey Significant writings that have influenced the curriculum: 1906-1981, by H.G. Shane and the 1994 yearbook of the National Society for the Study of Education.
A mythology has grown around the taxonomy, possibly due to many people learning about the taxonomy through second hand information. Bloom himself considered the Handbook,[1] "One of the most widely cited yet least read books in American education."[3]
Contents[hide] |
[edit] Domains
Key to understanding the taxonomy and its revisions, variations, and addenda over the years is an understanding that the original Handbook[1] in 1956 was intended only to focus on one of the three domains (as indicated in the domain specification in title: The Taxonomy of Educational Objectives: Handbook I: Cognitive Domain), but there was expectation that additional material would be generated for the other domains (as indicated in the numbering of the handbook in the title).The second volume, Handbook II: Affective Domain edited by David Krathwohl was published in 1964.[8]
There was no Handbook III for the Psychomotor domain published by the committee as the consensus was that (as college level academics) they lacked the necessary experience to do the job properly.[3] Substitute domain taxonomies have been published by various authors[9][10][11] to fill the gap.
Bloom also considered the initial effort to be a starting point, as evidenced in a memorandum from 1971 in which he said, "Ideally each major field should have its own taxonomy in its own language - more detailed, closer to the special language and thinking of its experts, reflecting its own appropriate sub-divisions and levels of education, with possible new categories, combinations of categories and omitting categories as appropriate."[5]
[edit] Cognitive
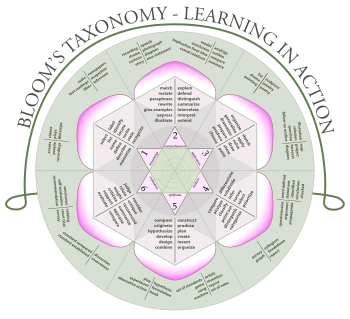
Skills in the cognitive domain revolve around knowledge, comprehension, and critical thinking of a particular topic. Traditional education tends to emphasize the skills in this domain, particularly the lower-order objectives.There are six levels in the taxonomy, moving through the lowest order processes to the highest:
- Knowledge
- Exhibit memory of previously-learned materials by recalling facts, terms, basic concepts and answers
- Knowledge of specifics - terminology, specific facts
- Knowledge of ways and means of dealing with specifics - conventions, trends and sequences, classifications and categories, criteria, methodology
- Knowledge of the universals and abstractions in a field - principles and generalizations, theories and structures
- Comprehension
- Demonstrative understanding of facts and ideas by organizing, comparing, translating, interpreting, giving descriptions, and stating main ideas
- Translation
- Interpretation
- Extrapolation
- Application
- Using new knowledge. Solve problems to new situations by applying acquired knowledge, facts, techniques and rules in a different way
- Analysis
- Examine and break information into parts by identifying motives or causes. Make inferences and find evidence to support generalizations
- Analysis of elements
- Analysis of relationships
- Analysis of organizational principles
- Synthesis
- Compile information together in a different way by combining elements in a new pattern or proposing alternative solutions
- Production of a unique communication
- Production of a plan, or proposed set of operations
- Derivation of a set of abstract relations
- Evaluation
- Present and defend opinions by making judgments about information, validity of ideas or quality of work based on a set of criteria
- Judgments in terms of internal evidence
- Judgments in terms of external criteria
[edit] Affective
Skills in the affective domain describe the way people react emotionally and their ability to feel another living thing's pain or joy. Affective objectives typically target the awareness and growth in attitudes, emotion, and feelings.There are five levels in the affective domain moving through the lowest order processes to the highest:
- Receiving
- The lowest level; the student passively pays attention. Without this level no learning can occur.
- Responding
- The student actively participates in the learning process, not only attends to a stimulus; the student also reacts in some way.
- Valuing
- The student attaches a value to an object, phenomenon, or piece of information.
- Organizing
- The student can put together different values, information, and ideas and accommodate them within his/her own schema; comparing, relating and elaborating on what has been learned.
- Characterizing
- The student holds a particular value or belief that now exerts influence on his/her behaviour so that it becomes a characteristic.
[edit] Psychomotor
Skills in the psychomotor domain describe the ability to physically manipulate a tool or instrument like a hand or a hammer. Psychomotor objectives usually focus on change and/or development in behavior and/or skills.Bloom and his colleagues never created subcategories for skills in the psychomotor domain, but since then other educators have created their own psychomotor taxonomies.[12] Simpson (1972) among other contributors, such as Harrow (1972) and Dave (1967), created a Psychomotor Taxonomy that helps to explain the behavior of typical learners or high performance athletes. The proposed levels are:
1. Perception: The ability to use sensory cues to guide motor activity. This ranges from sensory stimulation, through cue selection, to translation. Examples: Detects non-verbal communication cues. Estimate where a ball will land after it is thrown and then moving to the correct location to catch the ball. Adjusts heat of stove to correct temperature by smell and taste of food. Adjusts the height of the forks on a forklift by comparing where the forks are in relation to the pallet. Key Words: chooses, describes, detects, differentiates, distinguishes, identifies, isolates, relates, selects.
2. Set: Readiness to act. It includes mental, physical, and emotional sets. These three sets are dispositions that predetermine a person's response to different situations (sometimes called mindsets). Examples: Knows and acts upon a sequence of steps in a manufacturing process. Recognize one's abilities and limitations. Shows desire to learn a new process (motivation). NOTE: This subdivision of Psychomotor is closely related with the “Responding to phenomena” subdivision of the Affective domain. Key Words: begins, displays, explains, moves, proceeds, reacts, shows, states, volunteers.
3. Guided Response: The early stages in learning a complex skill that includes imitation and trial and error. Adequacy of performance is achieved by practicing. Examples: Performs a mathematical equation as demonstrated. Follows instructions to build a model. Responds hand-signals of instructor while learning to operate a forklift. Key Words: copies, traces, follows, react, reproduce, responds
4. Mechanism: This is the intermediate stage in learning a complex skill. Learned responses have become habitual and the movements can be performed with some confidence and proficiency. Examples: Use a personal computer. Repair a leaking faucet. Drive a car. Key Words: assembles, calibrates, constructs, dismantles, displays, fastens, fixes, grinds, heats, manipulates, measures, mends, mixes, organizes, sketches.
5. Complex Overt Response: The skillful performance of motor acts that involve complex movement patterns. Proficiency is indicated by a quick, accurate, and highly coordinated performance, requiring a minimum of energy. This category includes performing without hesitation, and automatic performance. For example, players will often utter sounds of satisfaction or expletives as soon as they hit a tennis ball or throw a football, because they can tell by the feel of the act what the result will produce. Examples: Maneuvers a car into a tight parallel parking spot. Operates a computer quickly and accurately. Displays competence while playing the piano. Key Words: assembles, builds, calibrates, constructs, dismantles, displays, fastens, fixes, grinds, heats, manipulates, measures, mends, mixes, organizes, sketches. NOTE: The Key Words are the same as Mechanism, but will have adverbs or adjectives that indicate that the performance is quicker, better, more accurate, etc.
6. Adaptation: Skills are well developed and the individual can modify movement patterns to fit special requirements. Examples: Responds effectively to unexpected experiences. Modifies instruction to meet the needs of the learners. Perform a task with a machine that it was not originally intended to do (machine is not damaged and there is no danger in performing the new task). Key Words: adapts, alters, changes, rearranges, reorganizes, revises, varies.
7. Origination: Creating new movement patterns to fit a particular situation or specific problem. Learning outcomes emphasize creativity based upon highly developed skills. Examples: Constructs a new theory. Develops a new and comprehensive training programming. Creates a new gymnastic routine. Key Words: arranges, builds, combines, composes, constructs, creates, designs, initiate, makes, originates.
[edit] Definition of Knowledge
In the appendix to Handbook I, there is a definition of knowledge which serves as the apex for an alternative, summary classification of the educational goals. This is significant as the Taxonomy has been called upon significantly in other fields such as knowledge management, potentially out of context| “ | Knowledge, as defined here, involves the recall of specifics and universals, the recall of methods and processes, or the recall of a pattern, structure, or setting. (Bloom et al. 1956 p 201) | ” |
1.00 Knowledge 1.10 Knowledge of Specifics 1.11 Knowledge of Terminology 1.12 Knowledge of Specific Facts 1.20 Knowledge of Ways and Means of Dealing with Specifics 1.21 Knowledge of Conventions 1.22 Knowledge of Trends and Sequences 1.23 Knowledge of Classifications and Categories 1.24 Knowledge of Criteria 1.25 Knowledge of Methodology 1.30 Knowledge of The Universals and Abstractions in a Field 1.31 Knowledge of Principles and Generalizations 1.32 Knowledge of Theories and Structures (Bloom et al. 1956 p 201-204)
[edit] Criticism of the Taxonomy
As Morshead[13] pointed out on the publication of the second volume, the classification wasn't a properly constructed taxonomy, as it lacked a systemic rationale of construction.This was subsequently acknowledged in the discussion of the original taxonomy by Krathwohl et al. in the revision of the taxonomy[5] and the taxonomy reestablished on more systematic lines. It is generally considered that the role the taxonomy played in systematising a field was more important than any perceived lack of rigour in its construction.
Some critiques of Bloom's Taxonomy's (cognitive domain) admit the existence of these six categories, but question the existence of a sequential, hierarchical link.[14] Also the revised edition of Bloom's taxonomy has moved Synthesis in higher order than Evaluation. Some consider the three lowest levels as hierarchically ordered, but the three higher levels as parallel.[5] Others say that it is sometimes better to move to Application before introducing concepts[citation needed]. This thinking would seem to relate to the method of problem-based learning.
[edit] Further reading
- Anderson, Lorin W. & Lauren A. Sosniak, eds. (1994), Bloom's Taxonomy: A Forty-Year Retrospective. Chicago National Society for the Study of Education
[edit] See also
- Educational psychology
- Educational technology
- Higher order thinking skills
- Mastery learning
- Physical education
- David Krathwohl
- Fluid and crystallized intelligence
- Information Hierarchy (DIKW)
[edit] References
- ^ a b c d Bloom, B. S., Engelhart, M. D., Furst, E. J., Hill, W. H., & Krathwohl, D. R. (1956). Taxonomy of educational objectives: the classification of educational goals; Handbook I: Cognitive Domain New York, Longmans, Green, 1956.
- ^ Bloom et al, (1956) p. 4 "The idea for this classification system was formed at an informal meeting of college examiners attending the 1948 American Psychological Association Convention in Boston. At this meeting, interest was expressed in a theoretical framework which could be used to facilitate communication among examiners. This group felt that such a framework could do much to promote the exchange of test materials and ideas about testing. In addition, it could be helpful in stimulating research on examining and on the relations between examining and education. After considerable discussion, there was agreement that such a theoretical framework might best be obtained through a system of classifying the goals of the educational process, since educational objectives provide the basis for building curricula and tests and represent the starting point for much of our educational research."
- ^ a b c Bloom, Benjamin S. Reflections on the development and use of the taxonomy in Anderson, Lorin W. & Lauren A. Sosniak, eds. (1994), Bloom's Taxonomy: A Forty-Year Retrospective. Chicago National Society for the Study of Education
- ^ Orlich, et al. (2004) Teaching Strategies: A Guide to Effective Instruction', Houghton Mifflin
- ^ a b c d L. W. Anderson, D. R. Krathwohl, Peter W. Airasian, Kathleen A. Cruikshank, Richard E. Mayer, Paul R. Pintrich, James Raths, and Merlin C. Wittrock (eds) (2000) A Taxonomy for Learning, Teaching, and Assessing: A Revision of Bloom's Taxonomy of Educational Objectives Allyn and Bacon
- ^ Anderson, L. & Krathwohl, D. A. (2001) Taxonomy for Learning, Teaching and Assessing: A Revision of Bloom's Taxonomy of Educational Objectives New York: Longman
- ^ Krathwohl, D. R. (2002). A revision of bloom's taxonomy: An overview. Theory into Practice, 41 (4), 212-218.
- ^ Krathwohl, D. R., Bloom, B. S., & Masia, B. B. (1964). Taxonomy of educational objectives; the classification of educational goals. Handbook II: The affective domain. New York: Longman, Green.
- ^ Simpson, E.J. (1972) The Classification of Educational Objectives in the Psychomotor Domain Washington DC: Gryphon House.
- ^ Harrow, A.J. (1972) A Taxonomy of the Psychomotor Domain New York:
- ^ Dave, R.H. (1970). Psychomotor levels. In RJ. Armstrong (Ed.) Developing and writing educational objectives (pp. 33-34). Tucson AZ: Educational Innovators Press.
- ^ Learning Domains or Bloom's Taxonomy - Donald R. Clark
- ^ Morshead, Richard W. (1965) Taxonomy of Educational Objectives Handbook II: Affective Domain. Studies in Philosophy and Education vol. 4 (1) pp. 164-170
- ^ Paul, R. (1993). Critical thinking: What every person needs to survive in a rapidly changing world (3rd ed.). Rohnert Park, California: Sonoma State University Press.
View page ratings
Rate this page
Saved successfully
Your ratings have not been submitted yet
Your ratings have expired
Thanks! Your ratings have been saved.
Thanks! Your ratings have been saved.
An account will help you track your edits, get involved in discussions, and be a part of the community.
or
Thanks! Your ratings have been saved.
========================================================================
http://zh.wikipedia.org/zh-hk/%E5%B8%83%E9%B2%81%E5%A7%86%E5%88%86%E7%B1%BB%E5%AD%A6
布魯姆分類學
維基百科,自由的百科全書
布盧姆分類學是美國教育心學家本傑明·布魯姆於1956年在芝加哥大學所提出的分類法,把教育者的教學目標分類,以便更有效的達成各個目標。根據布盧姆的理論析,知識可以分成以下三個範疇[1]:
態度範疇內的過程從低至高可分為五個層次:
布盧姆及他的同工並未有就此範疇提出過細目,但此後有不少教育家都嘗試提出他們認為技巧範疇應有的細目[2]。
- 認知範疇 (Cognitive Domain)
- 技巧範疇 (Psychomotor Domain)及
- 態度範疇 (Affective Domain)
目錄[隱藏] |
[編輯] 態度範疇
「態度範疇」描述人們在情感方面的反應方式、以及他們感受其他生物的苦痛與快樂的能力。態度方面的目標通常針對於態度、情感及感受方面的覺醒與成長。態度範疇內的過程從低至高可分為五個層次:
- 接受(Receiving):是態度範疇內最低層次的過程,學生只是被動的要求專注。若連這一層次也不能達到的話,可以說根本毫無學習可言。
- 反應(Responding):在這層次,學生不單只對於刺激作出反應,更可主動參與學習過程。
- 評價(Valuing):學生可對一件物件、一個現象或一份信息給予評價。
- 組織(Organizing):學生把不同的價值、信息及意念擺在一起,並利用他們本身的schema來將他們容納在一起。比較、關聯和引申所學過的內容。
- 內化(Characterizing):
[編輯] 技巧範疇
「技巧範疇」描述人們在真實的使用一件工具或儀器,例如搥子的能力。技巧範疇的目的通常專注於改變及行為與技巧的開發。布盧姆及他的同工並未有就此範疇提出過細目,但此後有不少教育家都嘗試提出他們認為技巧範疇應有的細目[2]。
[編輯] 認知範疇
認知範疇包括以下六種:- 知識
- 理解
- 應用
- 分析
- 綜合
- 評價
[編輯] 知識 (Knowledge)
知識指的是對於數據或信息的回憶。例如:- 牢記政策
- 從記憶裡向客人報價
- 習得安全守則
- 定義:defines
- 描述:describes
- 確認:identifies
- 明白:knows
- 分類:labels
- 表列:lists
- 配對:matches
- 命名:names
- 概述:outlines
- 回憶:recalls
- 辨識:recognizes
- 重覆:reproduces
- 選取:selects
- 描述:states
[編輯] 理解 (Comprehension)
[編輯] 應用 (Application)
[編輯] 分析 (Analysis)
[編輯] 綜合 (Synthesis)
[編輯] 評價 (Evaluation)
[編輯] 參看
[編輯] 參考
- ^ 菖蒲,(1994年),《我在小學的日子裏》
- ^ 詳見http://www.nwlink.com/~donclark/hrd/bloom.html。
- Taxonomy of Educational Objectives: The Classification of Educational Goals; pp. 201-207; B. S. Bloom (Ed.) Susan Fauer Company, Inc. 1956.
謝謝!您的評分已保存。
謝謝!您的評分已保存。
帳戶將幫助您跟蹤您所做的編輯,參與討論,並成為社區的一部分。
或者
謝謝!您的評分已保存。
========================================================================

沒有留言:
張貼留言